Refraction is the bending of light (it also happens with sound, water and other waves) as it passes from onetransparent substance into another.
This bending by refraction makes it possible for us to have lenses, magnifying glasses, prisms and rainbows. Even our eyes depend upon this bending of light. Without refraction, we wouldn’t be able tofocus light onto our retina
Change of speed causes change of direction
Light refracts whenever it travels at an angle into a substance with a different refractive index (opticaldensity).
This change of direction is caused by a change in speed. For example, when light travels from air into water, it slows down, causing it to continue to travel at a different angle or direction.
How much does light bend?
The amount of bending depends on two things:
- Change in speed – if a substance causes the light to speed up or slow down more, it will refract (bend) more.
- Angle of the incident ray – if the light is entering the substance at a greater angle, the amount of refraction will also be more noticeable. On the other hand, if the light is entering the new substance from straight on (at 90° to the surface), the light will still slow down, but it won’t change direction at all.
Refractive index of some transparent substances
Substance | Refractive index | Speed of light in substance | Angle of refraction if incident ray enters substance at 20º |
Air | 1.00 | 300 | 20 |
Water | 1.33 | 226 | 14.9 |
Glass | 1.5 | 200 | 13.2 |
Diamond | 2.4 | 125 | 8.2 |
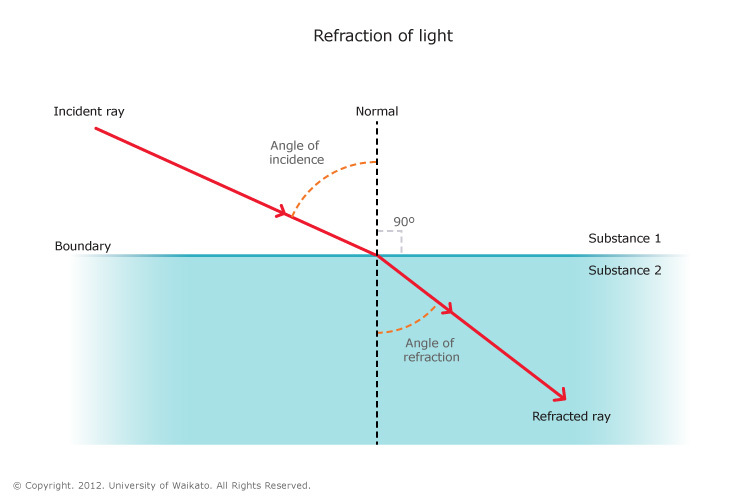
All angles are measured from an imaginary line drawn at 90° to the surface of the two substances This line is drawn as a dotted line and is called the normal.
If light enters any substance with ahigher refractive index (such as from air into glass) it slows down. The light bends towards the normal line.
If light travels enters into a substance with a lower refractive index (such as from water into air) it speeds up. The light bends away from the normal line.
A higher refractive index shows that light will slow down and change direction more as it enters the substance.


Good
ReplyDelete